SEARCH
— 葡萄酒 | 威士忌 | 白兰地 | 啤酒 —
— 葡萄酒 | 威士忌 | 白兰地 | 啤酒 —
 Introduction
IntroductionIn today’s rapidly evolving Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) landscape, industrial-grade 4G routers have emerged as critical network infrastructure components supporting digital transformation across various industries. Compared to standard consumer routers, industrial 4G routers differ fundamentally in design philosophy, hardware configuration, and functional implementation. This article provides an in-depth analysis of the core technical features of industrial-grade 4G routers, with special focus on their diverse interface design, high-performance processors, and robust data processing capabilities.
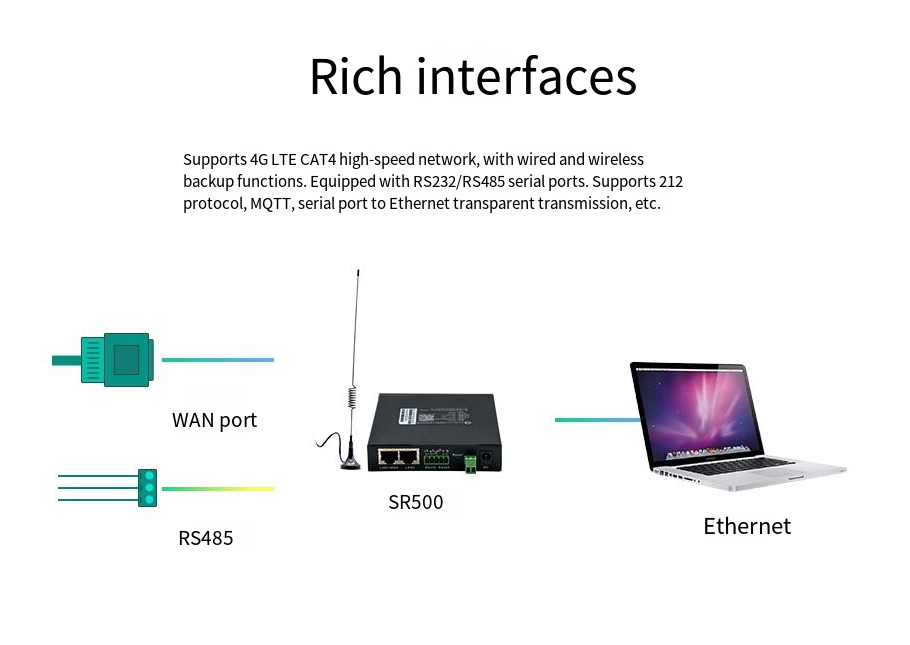
Industrial-grade 4G routers typically feature multiple types of wired interfaces to satisfy connectivity requirements across different industrial scenarios.Industrial Ethernet Interfaces: Unlike the plastic RJ45 interfaces found in consumer routers, industrial routers utilize metal-cased reinforced Ethernet interfaces with anti-loosening and anti-corrosion properties. These can withstand over 5,000 insertion cycles and operate in temperature ranges from -40°C to 85°C, ensuring stable performance in environments with vibration, high temperatures, and other harsh conditions.Serial Communication Interfaces: Industrial 4G routers commonly integrate multiple serial ports including RS232/RS485/RS422, enabling direct connection to PLCs, industrial controllers, sensors, and other traditional industrial equipment for data collection and transmission without requiring additional protocol conversion devices.Industrial Bus Interfaces: High-end industrial routers may also integrate CAN, PROFIBUS, Modbus, and other industrial fieldbus interfaces, allowing seamless integration with automated control systems and facilitating interconnection between industrial control networks and enterprise networks.
Multiple SIM Card Design: Industrial 4G routers typically employ dual or even quad SIM card designs, supporting automatic switching between different carrier networks to ensure communication reliability. Some premium models support global frequency bands, enabling use in different countries and regions.Multiple Antenna Technology: Equipped with 2-4 high-gain external antennas using MIMO technology to enhance signal transmission quality and effectively improve anti-interference capability in complex electromagnetic environments, ensuring stable operation even in areas with poor signal coverage.WiFi and IoT Protocol Support: Beyond 4G cellular networks, these routers integrate industrial-grade WiFi modules and support Bluetooth, ZigBee, LoRa, and other low-power IoT protocols, enabling multi-protocol integrated communications.
Industrial 4G routers utilize processors that fundamentally differ from those in standard commercial routers:Powerful Computing Performance: Mainstream industrial routers employ ARM Cortex-A series or Intel processors with clock speeds typically exceeding 1GHz. Multi-core designs provide enhanced parallel processing capabilities. Some high-end models feature quad-core 1.2GHz processors, delivering computing power several times greater than ordinary consumer routers.Reliability Design: Industrial-grade processors utilize industrial-quality chips with comprehensive quality certification systems and Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) exceeding 100,000 hours. They also incorporate low-power designs that effectively control heat generation and reduce system crash risks.Wide Temperature Characteristics: Supporting operating temperature ranges from -40°C to 85°C ensures stable operation in extreme climate conditions, meeting the requirements of outdoor and specialized industrial environments.
High-Speed Cache and Storage: Industrial routers typically come equipped with 128MB-1GB of high-speed DDR memory and 8GB-32GB eMMC or SSD storage, capable of storing large amounts of device data and system logs.Data Protection Mechanisms: Industrial-grade flash memory offers superior read/write durability and data retention capabilities. Combined with power-down protection design, these features ensure critical data is not lost during unexpected system power failures.
Dedicated Network Processing Units: High-end industrial routers integrate specialized NPUs (Network Processing Units) enabling high-speed data forwarding with throughput reaching 300-500Mbps, far exceeding the performance limits of ordinary 4G routers.QoS Traffic Control: Support for granular bandwidth management and priority scheduling ensures priority transmission of critical business data, meeting industrial control systems’ strict requirements for real-time performance and reliability.VPN Acceleration Engine: Built-in hardware encryption acceleration engines support multiple VPN protocols including IPsec, OpenVPN, and L2TP, with encryption transmission speeds exceeding 100Mbps, ensuring both security and efficiency in remote data transmission.
Local Data Analysis: Modern industrial routers function not just as transmission channels but as edge computing nodes, supporting data filtering, aggregation, and preliminary analysis at the device level, reducing cloud transmission data volume and lowering network load and latency.Open Software Platform: Built on Linux or real-time operating systems, these routers provide open APIs and SDK development toolkits, allowing users to develop custom applications and services to implement specialized industry-specific functions.Containerized Deployment: Advanced industrial routers support container technologies like Docker, enabling flexible deployment of AI inference, protocol conversion, data preprocessing, and other microservices, transforming them into truly intelligent edge gateways.
Dual Power Redundancy: Support for AC/DC dual power input ensures system operation continues normally even when one power source fails.Watchdog Mechanism: Hardware-level watchdog timers monitor system operating status and automatically restart to restore operation when system anomalies occur, ensuring long-term stable operation.Link Backup and Load Balancing: Support for redundant backup and load balancing between 4G and wired networks or multiple SIM cards ensures uninterrupted network connectivity.
Wide Temperature Design: Industrial-grade components support operating temperatures from -40°C to 85°C, adapting to various extreme environments.High Protection Rating: Metal enclosure designs with IP30-IP67 protection ratings offer dust, water, and shock resistance for reliable operation in harsh industrial environments.Anti-Interference Design: Electromagnetic compatibility design supporting 8KV air discharge/6KV contact discharge protection effectively resists electromagnetic interference.
In smart factory environments, industrial-grade 4G routers serve as critical communication nodes connecting hundreds of CNC machines, robots, and sensor devices, collecting production data in real-time and transmitting it to enterprise cloud platforms. With powerful processors and high-capacity memory, these routers can simultaneously process up to 500 TCP connections and handle tens of thousands of device data points per second, ensuring real-time monitoring and analysis of production line operational status.
In distributed energy equipment monitoring, industrial routers collect operational parameters from wind turbines and photovoltaic equipment through serial ports, perform data preprocessing and anomaly detection using edge computing functions, and transmit only valuable data to central monitoring platforms via 4G networks, significantly reducing data transmission costs while improving response times for abnormal situations.
Industrial-grade 4G routers, with their rich interface design, high-performance processors, and powerful data processing capabilities, have become essential components of industrial internet infrastructure. As edge computing technology continues to develop, industrial routers will further evolve toward intelligence and integration, providing increasingly reliable technical support for digital transformation across various industries. When selecting industrial routers, organizations should comprehensively consider interface types, processing performance, protection ratings, and other factors based on specific application scenario requirements to select the most appropriate product solution.
Mo